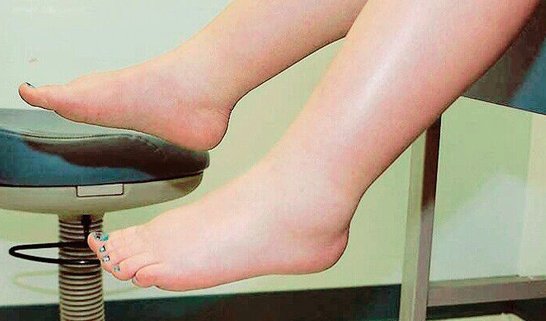
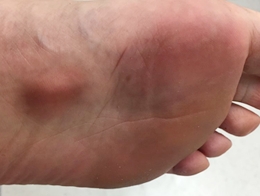
Swollen Feet
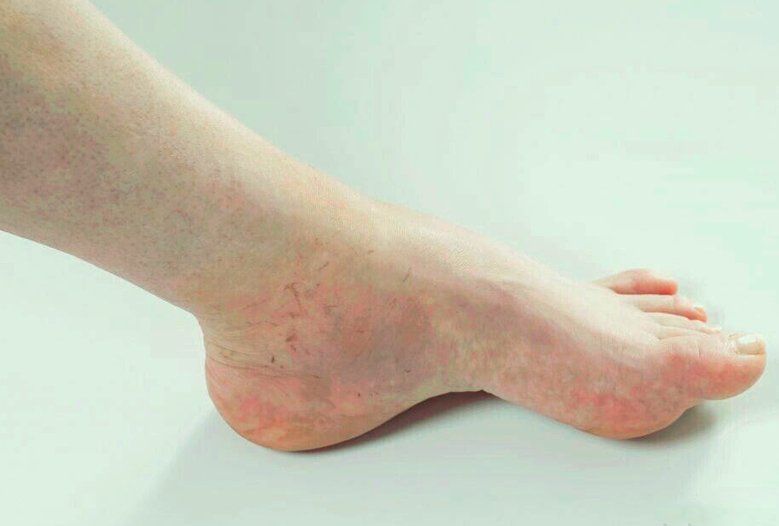
Swelling of the feet refers to an increase in the size of the foot or both feet. It is a fairly common occurrence that may involve both feet or only one. While only feet may swell, most often swollen feet are accompanied by swollen ankles, or even other swollen body parts.
Causes of Swollen Feet
Swollen feet have a myriad of causes ranging from the fairly harmless to life threatening conditions. Causes of swollen feet include:
Dependent swelling
This refers to the swelling that is often observed following long periods of standing up or sitting down. While it may be an indicator of underlying disease, it is most often a normal effect of gravity resulting in fluid pooling at the lower peripheries.
Angioedema
Occasionally, swollen feet may be a result of angioedema. Angioedema refers to accumulation of fluids, mostly beneath the upper layers of the skin, resulting in swelling. While it may occur in isolation in the feet, it is more often noticed in other parts of the body as well. In most cases, angioedema occurs as an allergic reaction perhaps to medication.
Lymphedema
Lymphedema refers to the accumulation of fluid that contains a lot of protein within the spaces that surround every cell. Because proteins are highly osmotic-meaning they easily attract water across permeable barriers, the accumulation of such fluid results in more fluid being pulled into this spaces. This results in increased swelling. Lymphedema may be primary, meaning that it may run in families. Therefore, if a child or a new born has swollen feet, and several other members of the family have swollen feet, the child-and the other members of the family-may be suffering from primary lymphedema. Lymphedema may also be secondary, for example, in the case of elephantiasis – a form of lymphedema characterized by massive limb swelling among other signs and symptoms.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy is a very common cause of swollen feet. Swollen feet in pregnancy can be explained by increased blood pooling around the lower extremities. In pregnancy, as the baby continues to grow, the womb continues increasing in size and thus, presses upon some veins found in the pelvic region. This results in impaired return of blood from the legs. Consequently, there is increased blood in the legs, which may result in fluid leaking out of the vessels, thus swelling.
Infections of the feet
Swollen feet because of infection
Most infections involving the foot tend to present with swelling of the feet. The most common is cellulitis. Cellulitis is an inflammation (which is a localized reaction by the body mostly due to injury including infection) affecting the tissue found just beneath the skin called the “subcutaneous tissue”. Unlike most of the above mentioned causes of foot swelling, cellulitis will most often affect only one foot. Another infection is necrotizing fasciitis. This is an inflammation of fascia – a thin glove like covering of muscles – and other subcutaneous tissue that often results in death of any infected tissue.
Trauma
One of the most common reasons as to why trauma leads to swollen feet is the increased susceptibility to infections. However, even on its own, trauma may lead to swelling as occurs in burns. Swelling following trauma can be loosely termed compartment syndrome. This involves swelling of the compartments within which muscles and blood vessels are held.
Diabetes Mellitus
While diabetes mellitus may result in swollen feet through increased susceptibility to infection, it also causes swollen feet in the absence of infection. In diabetes mellitus, there is often increased levels of blood glucose. Glucose, like proteins, acts as a powerful agent of osmosis. Therefore, in high concentrations of glucose, there is often increased water retention in the body. This may result in swelling, not only in the feet, but also in the entire body, resulting in perceived weight gain.
Blood clots
The presence of blood clots, particularly in the veins of the foot usually results in swelling of one foot. Blood clots, if big enough, may occlude the veins preventing blood from flowing back. There is blood retained within the foot, resulting in increased fluid leaking out of the vessels, thus, swelling.
Other diseases
Swollen feet may be an indicator of much more serious diseases, especially if accompanied by certain signs and symptoms. Swollen feet may be seen in people who suffer from kidney, liver or heart disease. Therefore, swollen feet that do not resolve with the home remedies or medication may point to a more serious underlying cause and medical help should be sought as soon as possible.
Signs and Symptoms of Swollen feet
- The most common symptom is feet which are increased in size. If only one foot is swollen, the swollen foot can be compared with the normal foot. If both feet are swollen, the extent of the swelling may be harder to estimate.
- Another common symptom is pain. Pain in the presence of swollen feet may be an indicator of cellulitis, necrotizing fasciitis, angioedema or trauma as the cause of the swelling.
- Local redness of the skin around the swelling is common in cellulitis, necrotizing fasciitis and trauma, but may be absent in angioedema.
- There may be a localized increase in temperature in cases of foot swelling due to cellulitis, while angioedema usually presents with a burning sensation which is often only around the swollen area.
- In lymphedema, there may be associated infections and unexplained fatigue.
Home Remedies
There are certain measures one can take before or even after seeking medical treatment. These include:
- Rest: This is useful in the case of dependent swelling and pregnancy. Rest enables the body to try and restore itself, especially as these causes of swollen feet usually are normal.
- Elevation of the legs: This is helpful in most of the cases of foot and ankle swelling. Elevation of the legs enables blood to flow back to the heart with minimal obstacles. The ideal elevation is about two or three well fluffed pillows to ensure that the legs are above the head and thus the heart while lying on a flat surface.
- Reducing the amount of salt taken: This may be tried especially in those who have early signs of either kidney or cardiac disease. Salt contains sodium, which is usually key in water retention. Therefore, if sodium intake is reduced, there may be an overall reduction in the amount of water retained in the body, thus reduction in the swelling.
- Regular cleaning of the swollen foot: This is mostly a preventative measure. Regular cleaning of the foot would prevent infection as swollen feet are prone to infection. It may also help remove dead tissue-although this is best done by someone who has adequate information and training on how to do so.
Certain home remedies are effective for certain causes of swollen feet. For example, in lymphedema, some relief may be achieved by losing weight if the person suffering is overweight. People with lymphedema may also benefit from the use of compression socks.
However, as a general rule, anyone who has swollen feet should avoid wearing tight clothes as these may further impair blood flow.
Treatment
For most cases, the treatment will depend on the underlying cause. However, for dependent swelling and pregnancy as causes of swollen feet, the above home remedies should be sufficient.
- Angioedema: The primary step would be to stop exposure to the allergen if one is present. The doctor may instruct on the use of medication. Most commonly, epinephrine. Corticosteroids and antihistamines may be recommended. Surgery is very rarely required, and even then, it is only in very severe cases.
- Lymphedema: Commonly used medication for lymphedema include coumarin and albendazole. Due to the increased susceptibility to infection in people with lymphedema, they may also require antibiotics like penicillin G and clindamycin.
- Foot Infections: Cellulitis is commonly treated using oral antibiotics including quinolones, cephalosporins and penicillins. It also often requires debridement, which is removal of dead tissue. Necrotizing fasciitis requires the use of broad spectrum antibiotics and debridement. For infections of the feet to heal properly, it is essential that they are detected early and adequately treated.
- Trauma: For trauma, there are various indications based on the type of trauma that was incurred. Most often, surgery is the preferred management.
- Diabetes mellitus: In diabetes mellitus, it is essential that the blood sugar levels be regulated and maintained within normal levels. In most cases, this will result in resolution of the swollen feet.
- Blood clots: Medical treatment of blood clots requires use of medication that can break down the clot and prevent more from forming. Very rarely, surgery may be indicated.
- Liver, kidney and heart disease: These require a treatment that caters specifically to the affected person. However, in most cases, the doctor may recommend a diuretic, which is medication that causes increased loss of water from the body.